Anxiety is a normal feeling that most people have in response to stressful or unexpected events. It can be helpful when it helps us to resolve complex problems or keep us from danger.
Anxiety becomes problematic when it affects our normal day-to-day functioning, distracts us from more important issues, or becomes overwhelming and persistent for no apparent reason.
Picking the proper medications for anxiety disorder can be tricky; we’re here to help. Like you, each medication for anxiety disorder is different, so it’s best to know them all before deciding.
Every medicine has its unique characteristics, distinguishing it from other medications. The differences are about its
- Duration of action (Peak effect and elimination)
- Dosage
- Side effects / Adverse effect profile
- Contraindications
Not the same medicine and exact dosage are suitable for everyone. Still, years of research help identify and select the best possible medications for anxiety disorder for a specific patient.
List of medications for anxiety disorder:
Multiple approaches to treating anxiety disorders may be necessary for a successful outcome. The aim of treatment is different for different patients.
Some patients need treatment for short-term attacks. Some need psychological therapy with antidepressants to achieve long-term effects and better control over anxiety.
Following are the medications for anxiety disorder:

Benzodiazepines:
Benzodiazepines are immediate acting drugs and are used in need for a quick response to severe anxiety attacks. Medicines in this class vary primarily related to their potency. They have a slight variation in their effect.
All benzodiazepines exhibit the following effects;
- Sedative
- Anxiolytic
- Muscular relaxant
- Hypnotic
- Anti-convulsant effect
These are absorbed rapidly in the brain and produce their effect.
Benzodiazepines Drugs:
Following drugs are included in benzodiazepines;
|
Sr No. |
Drug Name |
Dosage (mg/day) |
|
1 |
Alprazolam |
0.5-1.5 mg |
|
2 |
Chlordiazepoxide |
30 mg |
|
3 |
Clonazepam |
2-4 mg |
|
4 |
Diazepam |
5-30 mg |
|
5 |
Lorazepam |
1-4 mg |
|
6 |
Oxazepam |
30 mg |
|
7 |
Temazepam |
10-20 mg |
Diazepam is considered the base agent, and the equivalency of other drug dosages is compared to 10mg of diazepam activity.
Due to the side effects and withdrawal problems of Benzodiazepines, antidepressants are used, which are more effective in treating anxiety than benzodiazepines and have fewer problems than benzodiazepine therapy.
These are used in the short term treatment of:
- Panic Disorder
- Generalized anxiety GAD
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD
- Social anxiety disorder SAD
Adverse Effects / Side Effects of Benzodiazepines:
The adverse effects of Benzodiazepines are pretty common due to their central nervous system inhibition. These adverse effects commonly include;
- Confusion
- Amnesia
- Light-headedness
- Drowsiness
- Unusual increase in aggression
- Increased risk of Falls
- Increased risk of Road Accidents due to impaired concentration and drowsiness
- But these above symptoms subside with the continuous therapy of 2-4 weeks.

Antidepressants:
Antidepressants have been used to treat anxiety disorders. Although they may not work as fast as benzodiazepines, they can be effective and have fewer side effects than benzodiazepines.
Unlike benzodiazepines, the antidepressant medications for anxiety disorder take a while to show their effect, usually in weeks.
As antidepressant therapy takes time to show its effects, a high dose is usually given at the start. An increase in anxiety symptoms is observed due to a delay in response.
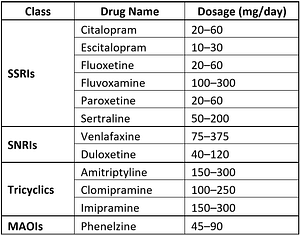
Antidepressants are used as first-line agents for the treatment of Anxiety. The antidepressants are classified into:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRIs):
These are the most common antidepressants used clinically for the treatment of different types of anxiety disorders like;
- Panic Disorder
- Generalized anxiety GAD
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder PTSD
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD
- Social Anxiety Disorder SAD
Adverse effects of SSRIs:
The adverse effects of SSRIs include
- Gastrointestinal Upset, Diarrhoea, Nausea
- Loss of Libido
- Diminished sexual function and interest
- Delayed orgasm
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Weight Gain (particularly with paroxetine
These above mentioned adverse effects reduce with time as therapy is continued.
Agents include in SSRIs
- Escitalopram
- Citalopram
- Fluoxetine
- Fluvoxamine
- Paroxetine
- Sertraline
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs):
These are licenced for the treatment of:
- Generalized anxiety GAD
- Social Anxiety Disorder
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD
Adverse effects of SNRIs:
These exhibit many side effects, same as SSRIs but also shows additional side effects related to norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. These are
- Increased Blood pressure
- Increased agitation
- Insomnia
Agents Include in SNRIs:
- Venlafaxine
- Duloxetine
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
This class of antidepressants was used commonly to treat anxiety before introducing SSRIs and SNRIs.
They are now used as a second line of agent for the treatment of anxiety for those patients who seems to get no benefits from the use of SSRIs and SNRIs.
The second choice for treatment is their poor tolerability compared to newer agents (SSRIs and SNRIs), difficulty in dose adjustment, and high chances of toxicity.
They are mainly used for their sedative property which is helpful for the treatment of Anxiety. These are used for:
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD
- Panic disorder
- Posttraumatic stress disorder PTSD
Adverse effects of TCAs:
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Urinary retention
- Blurred vision
- Confusion
- Produces cardiac arrhythmia if high doses are used
They should be avoided in patients with cardiac disease and patients having suicidal tendencies.
Agents Include in TCAs:
- Amitriptyline
- Clomipramine
- Imipramine
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MOI):
These were first introduced in the 1950s but are rarely used due to their lethal interaction with food, toxicity, and drug interactions. These were used to treat
- Social Anxiety
- Panic disorders
- Posttraumatic stress disorder PTSD
These are used only as a third-line treatment option when other antidepressants are not producing any effects, but only under the guidance of a specialist.
Agents include in MOIs are:
- Moclobemide
- Phenelzine
Doses of Antidepressant medications for anxiety disorder
Other medications for anxiety disorder:
Apart from benzodiazepines and antidepressants, there are other medicines which are used for the treatment of anxiety. These are not anxiolytics but help in reducing symptoms of anxiety.
Pregabalin:
It is licenced to be used to treat generalized anxiety disorder and shows its effect within one week of usage. It is also combined with SSRIs and SNRIs when treatment alone is not proven effective.
Side effects include: Dizziness, Somnolence, Nausea
Buspirone:
It is approved to be used in the short term to treat generalized anxiety only for the short term duration. It is often used in those patients who have no effect with first-line anxiolytics.
Propranolol:
It is a beta-blocker and is used mainly to treat PTSD symptoms. Propranolol is not an anxiolytic, but it is used for treating and controlling physical symptoms of PTSD, including:
- Increased heartbeat or Palpitations
- Tremors
- Shortening of Breath
- Sweating
Hydroxyzine:
It is approved to be used for its sedating effects when needed to treat generalized anxiety (GAD).
Anxiety Medicine List (Summary)

Summary:
Anxiety is one of the conditions we face multiple times in our lives. Anxiety becomes crippling when it becomes out of control and becomes a disease condition.
Treatment of anxiety is a must for living a healthy and joyous life.
There are different medications for anxiety disorder; these are used to treat anxiety and its symptoms.
Therapy used to treat anxiety varies from patient to patient. Choosing the best suitable treatment and tailoring it per the patient’s need is the only way to treat different types of anxiety.
Benzodiazepines are the most commonly prescribed medicines. They are approved to treat anxiety and its symptoms. Patients often abuse these because they are addictive.
Antidepressant therapy must be used with caution and continued as per the doctor’s advice and supervision.
Patients should consult with their physician about their treatment for anxiety before starting any new medicine. The physician should also check for any possible side effects of drugs and advise the patient about the risks of misuse or abuse of these medicines and appropriate dosages.